Cancer: Tumor transition states
Researchers at the Université libre de Bruxelles, ULB define for the first time the tumor transition states occurring during cancer progression and identify the tumor cell populations responsible for metastasis.
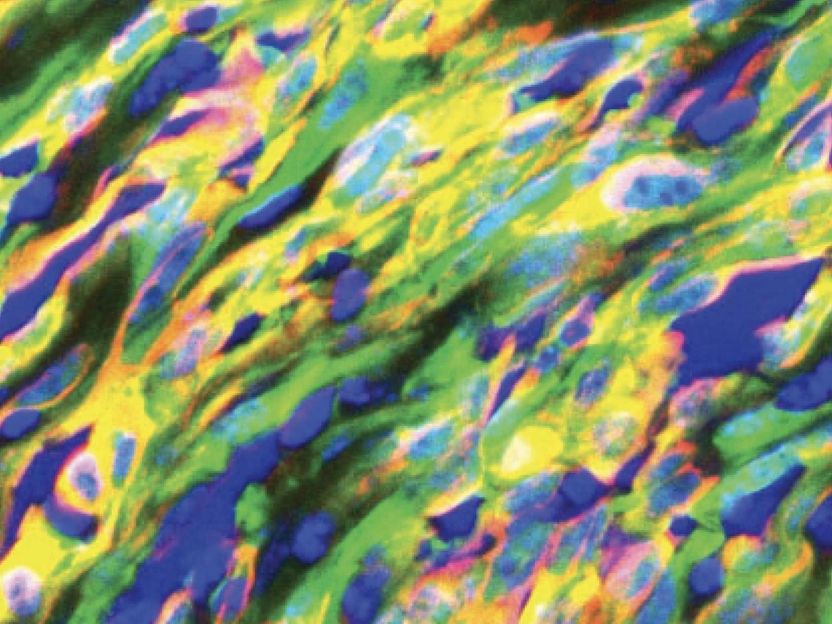
Researchers at the Université libre de Bruxelles define for the first time the tumor transition states occurring during cancer progression and identify the tumor cell populations responsible for metastasis.
ULB Cédric Blanpain
Tumor heterogeneity describes the differences between different cells within a given tumor. These differences have major implications for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of cancer patients. Different mechanisms have been proposed to account for tumor heterogeneity such as epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process in which epithelial tumor cells loose their adhesion and acquire mesenchymal migratory properties that are associated with metastasis and resistance to therapy. Cells with different degree of EMT could exhibit different metastatic potential, although this possibility has not been investigated so far.
In a study a research team led by Prof. Cédric Blanpain, MD/PhD, WELBIO investigator and Professor at the Université libre de Bruxelles, Belgium, identified for the first time, the different tumor transition states occurring during cancer progression and identified subpopulations of tumor cells responsible for metastasis in skin squamous cell carcinoma, the second most frequent cancer worldwide, and breast cancer, the most frequent cancers in women.
Ievgenia Pastushenko and colleagues used state of the art genetic mouse model of skin and breast cancers that undergo spontaneous EMT. By screening hundreds of monoclonal antibodies recognizing cell surface molecules and performing single cell RNA sequencing, they uncovered the existence of at least 7 different tumor subpopulations in skin and breast tumors that represent different EMT states: from completely epithelial or well differentiated to completely mesenchymal or undifferentiated states, passing through intermediate hybrid states.
The authors demonstrated that not all tumor cells are functionally equivalent and equally metastatic and that tumor cells with hybrid EMT phenotype -those co-expressing both epithelial and mesenchymal markers- are responsible for lung metastasis. "It was particularly exciting to observe that, in contrast to what one would expect, the tumor cells in the early stage of EMT with intermediate epithelial and mesenchymal hybrid phenotype, rather that tumor cells that underwent complete EMT, are the most metastatic populations", comments Ievgenia Pastushenko, the first author of the study.
In addition, this study led to the identification of the gene regulatory network and the tumor microenvironments that control the different tumor transition states. "The identification of these different tumor transition states presenting different functional characteristics such as proliferation, invasion, and metastatic potential across a wide range of mouse and human cancers has a very important implications for developing new strategies to block tumor progression and metastasis. It is likely that these different tumor transition states are also important for the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy and radiotherapy", explains Prof. Cédric Blanpain.
Original publication
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous