“Stretching Rack” for Cells
An ingenious device, only a few micrometers in size, enables to study the reaction of individual biological cells to mechanical stress
The behavior of cells is controlled by their environment. Besides biological factors or chemical substances, physical forces such as pressure or tension are also involved. Researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Heidelberg University developed a method that enables them to analyze the influence of external forces on individual cells. Using a 3D printing process, they produced micro-scaffolds, each of which has four pillars on which a cell is located. Triggered by an external signal, a hydrogel inside the scaffold swells and pushes the pillars apart, so that the cell must “stretch.”
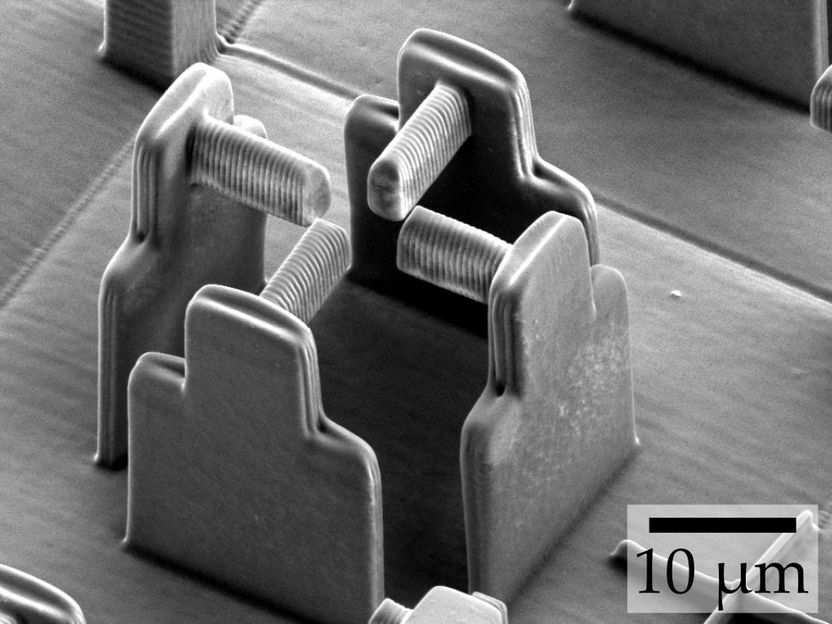
Electron micrograph of the “empty” scaffold (without hydrogel) that an international research team used to deform individual cells.
Marc Hippler, KIT

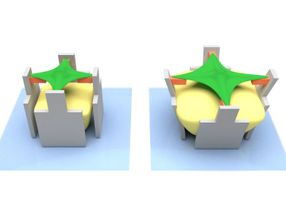
The hydrogel (yellow) swells and pushes the micro-scaffold (grey) apart – together with the cell-attracting bar (orange). This deforms the cell (green).
Marc Hippler, KIT
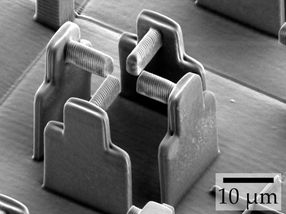
Many cellular biological processes, such as wound healing or the development of tissue, are strongly influenced by the properties of their environment. Cells react, for example, to biological factors or chemical substances. However, research is increasingly focusing on physical forces acting on the cells: How exactly do the cells adapt to these forces?
Within the framework of the German-Japanese University Consortium HeKKSaGOn and in cooperation with Australian scientists, the 3DMM2O team has taken a particularly ingenious approach to this question. For the production of their cell “stretching racks” they used “direct laser writing”, a special 3D printing process in which a computer-controlled laser beam is focused into a special printer ink liquid. Its molecules react only at the exposed areas and form a solid material there. All other areas remain liquid and can be washed away. “This is an established method in our Cluster of Excellence for building three-dimensional structures – on the micrometer scale and below,” explains Marc Hippler from the KIT Institute of Applied Physics, lead author of the publication.
In the current case, the researchers used three different printer inks: The first ink, made of protein-repellent material, was used to form the actual micro-scaffold. Using a second ink of protein-attracting material, they then produced four horizontal bars that are connected to one of the scaffold pillars each. The cell is anchored to these four bars. The real showstopper, however, is the third ink: The scientists used it to “print” a mass inside the scaffold. If they then add a special liquid, the hydrogel swells. It thus develops a force sufficient to move the pillars – and the bars with them. This, in turn, has the effect of stretching the cell that is fixed to the bars.
Cells counteract deformation
The scientists of the Cluster of Excellence placed two completely different cell types on their micro stretching rack: human bone tu-mor cells and embryonic mouse cells. They found that the cells counteract the external forces with motor proteins and thus greatly increase their tensile forces. When the external stretching force is removed, the cells relax and return to their original state. “This be-havior is an impressive demonstration of the ability to adapt to a dynamic environment. If the cells were unable to recover, they would no longer fulfill their original function – for example wound closure,” says Professor Martin Bastmeyer from the Zoological Institute of KIT.
As the team further discovered, a protein called NM2A (non-muscle myosin 2A) plays a decisive role in the cells' response to mechani-cal stimulation: Genetically modified bone tumor cells that cannot produce NM2A were barely able to counteract the external defor-mation.
Original publication
Marc Hippler, Kai Weißenbruch, Kai Richler, Enrico D. Lemma, Masaki Nakahata, Benjamin Richter, Christopher Barner-Kowollik, Yoshinori Takashima, Akira Harada, Eva Blasco, Martin Wegener, Motomu Tanaka, Martin Bastmeyer; "Mechanical Stimulation of Single Cells by Reversible Host-Guest Interactions in 3D Micro-Scaffolds"; Science Advances; 2020
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.

Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.