Electron bubbles modelled from X-ray laser data
An international team of scientists uncovers a groundbreaking model for the effects of radiation in water systems
What happens when radiation hits water? This is a question that has an impact every time you get an X-ray at the doctor’s office, given you are mostly made of water. A team of theoretical physicists at DESY has worked on data taken by colleagues from Argonne National Laboratory in the US at the LCLS X-ray laser in California to get a better answer to this question. What they found may settle a controversy in physics about the presence of free electrons in water and how they behave at very short time scales: the electrons, unbound to atoms, become sequestered in bubbles in cage-like structures between individual water molecules. These findings are reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
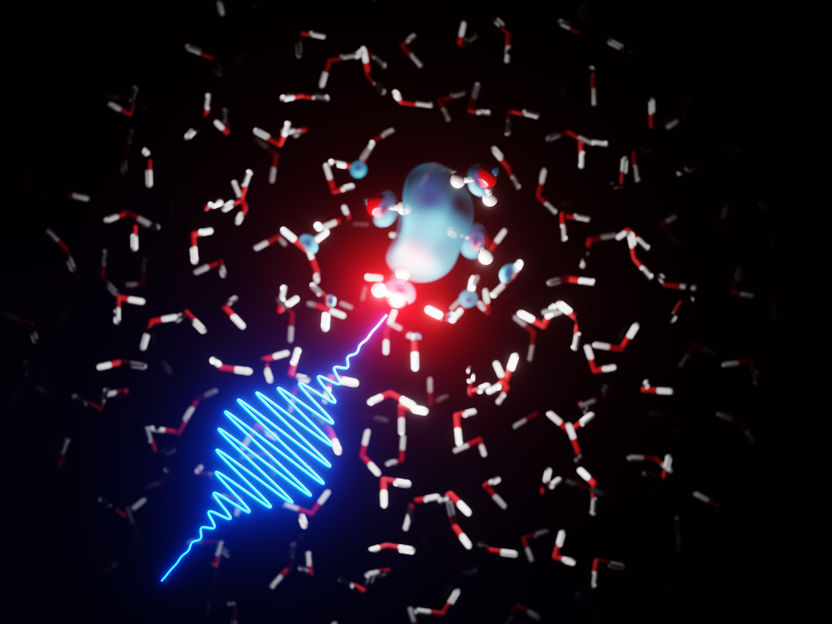

Using the X-ray laser LCLS in California, the experiment team, led by Argonne scientist Linda Young, could image the structures of the water molecules surrounding the electron bubbles. The theory team in Hamburg, led by CFEL senior scientist Ludger Inhester was able to model how the bubble itself behaved using the experiment team's data.
DESY/ Arturo Sopena Moros
In their work at LCLS at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, the experimental team, led by Argonne scientist Linda Young, saw odd signatures associated with the water molecules excited by lasers and imaged by the X-ray laser. They found structures among the molecules using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. In order to gain a better understanding of what these results meant, the experiment team turned to theoretical physicists in Hamburg.
A team led by DESY scientist Ludger Inhester of the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science examined the data and began making models from the data in coordination with the experimental team. Together their findings show that the free electrons in the water form bubble structures that are then caged in by water molecules, similar to how chemicals are solvated in water at the molecular level. In particular, the DESY team managed to show the process behind this solvation of electrons in the water and its parameters.
“It turns out that the dissolution process and thus the formation of the cage structures is remarkably sensitive to temperature changes in the water,” says Arturo Sopena, the first author of the study. The new insights into the solvation process show that the electron, which at first can be found over a wide area amongst the water molecules, docks onto specific hydrogen bonding patterns that occur in the molecular liquid water and then “burrows” deeper into a very narrow area within the water structure. This “burrowing” and the associated reorientation of the neighbouring water molecules takes place remarkably quickly and is completed within 100 femtoseconds, where a femtosecond is a quadrillionth of a second. The bubble, which is about 50 billionths of a metre wide, disassociates within several picoseconds, or a trillionth of a second.
“How does water react when exposed to radiation? This is a vital question,” says Inhester. “These are the first chemical reaction steps that are driven by the radiation that also determine the following radiation chemistry, which applies as well to biological material.”
Original publication
Arturo Sopena Moros, Shuai Li, Kai Li, Gilles Doumy, Stephen H. Southworth, Christopher Otolski, Richard D. Schaller, Yoshiaki Kumagai, Jan-Erik Rubensson, Marc Simon, Georgi Dakovski, Kristjan Kunnus, Joseph S. Robinson, Christina Y. Hampton, David J. Hoffman, Jake Koralek, Zhi-Heng Loh, Robin Santra, Ludger Inhester, Linda Young; "Tracking Cavity Formation in Electron Solvation: Insights from X-ray Spectroscopy and Theory"; Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024-1-25
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!