Chemists develop faster, more efficient protein labeling
North Carolina State University researchers have created specially engineered mammalian cells to provide a new "chemical handle" which will enable researchers to label proteins of interest more efficiently, without disrupting the normal function of the proteins themselves or the cells in which they are found.
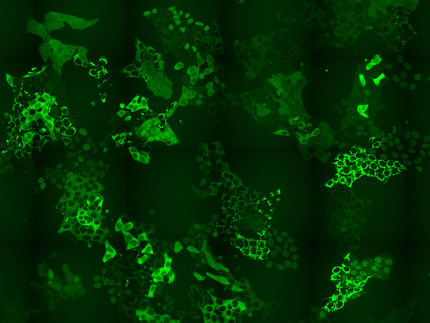
Protein labeling is used by researchers in a variety of fields to help them understand how these important molecules affect the normal functioning of cells. Currently, proteins are labeled for study simply by fusing them to other fluorescent proteins, which allows researchers to use microscopy to track their movements through a cell. This approach has several drawbacks, however, not least being that the fluorescent proteins are often large enough to affect the function of the protein of interest.
Dr. Alex Deiters, associate professor of chemistry, along with colleague Dr. Jason Chin of the Laboratory of Molecular Biology at the Medical Research Council in Cambridge, U.K., have developed a way to attach a fluorophore – a fluorescent molecule about 20 times smaller than the fluorescent proteins currently in use – to a protein that is expressed in a mammalian cell.
Deiters and Chin developed a special 21st amino acid that they added to cells that were specially engineered to incorporate this amino acid into the protein they wanted to study (there are normally only 20 amino acids). This 21st amino acid has a "chemical handle" that only reacts with a specifically designed fluorophore, but not any cellular components. According to Deiters, "The reaction between the modified protein and the fluorophore is extremely fast, high yielding, and generates a stable link between both reaction partners. This novel methodology enables future cell biological studies that were previously not possible."
"We found that our approach gave us a higher yield of labeled proteins and that the binding reaction was 50 times faster than with current methods," Deiters says. "Additionally, it took less reagent to complete the reaction, so overall we have a faster, more efficient method for protein labeling, and less chance of interfering with the normal function of the proteins and cells being studied."
Original publication
Alexander Deiters, Jessica Torres-Kolbus, Chungjung Chou, Jason W. Chin, Kathrin Lang; "Genetically encoded norbornene directs site-specific cellular protein labelling via a rapid bioorthogonal reaction"; Nature Chemistry.
Most read news
Original publication
Alexander Deiters, Jessica Torres-Kolbus, Chungjung Chou, Jason W. Chin, Kathrin Lang; "Genetically encoded norbornene directs site-specific cellular protein labelling via a rapid bioorthogonal reaction"; Nature Chemistry.

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.