Tracking Tiny Particles
Scientists at the University of Tübingen head a new international project to develop an electrochemical sensor to detect and analyze nanoparticles in commercial products.
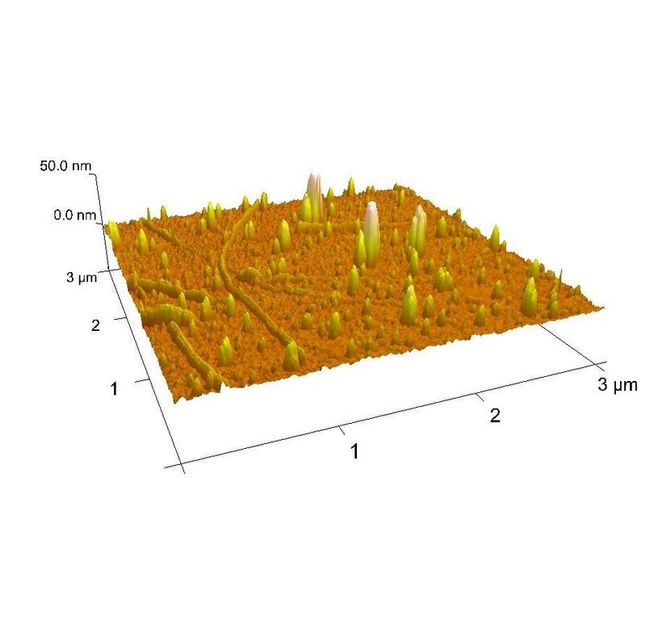
Nanostructured surface with detection elements.
IPTC, Universty of Tübingen
They are found in cosmetics and paints, and even help keep fruit fresh – nanoparticles, with their antimicrobial qualities, are being introduced into more and more everyday products. Yet there has been little research into their possible side effects. Scientists at the University of Tübingen are spearheading a new international project which examines nanoparticles and what they can do.
Ten institutions in six different countries are participating in the project, known as INSTANT (Innovative Sensor for the fast Analysis of Nanoparti-cles in Selected Target Products). They are developing a sensor which will be able to test for nanoparticles quickly and cost-effectively even in complex media such as milk or blood. Optical and electrochemical pro-cesses are being combined to quickly classify the particles and to evalu-ate their characteristic sizes.
Researchers in Tübingen at the Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry (Prof. Dr. Günter Gauglitz) and at the commercial start-up “Bi-ametrics” are developing innovative label-free sensors to determine bio-molecular effects in the areas of health, food safety, and environment analysis, and also gaining valuable experience in this relatively unex-plored field.
Nanotechnology has in recent years become an increasingly important focus of research. Particles only measurable on the nanoscale (one na-nometer = one millionth of a millimeter) have special characteristics, mak-ing them useful for a broad spectrum of applications. Yet the advantages of their relatively large surface area and altered material properties come with unpredictable risks.
Because they are widely added to cosmetics such as crèmes and sprays, textiles, foodstuffs, drinks, packaging and paints and lacquers, we all come into daily contact with nanoparticles. As yet, manufacturers are not obliged to list the addition of nanoparticles to their products; but it is not yet known what effect they can have on living organ-isms and the environment. The particles are so small that they can be absorbed into the blood-stream via the lungs, traveling to all parts of the body including the brain.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has started drafting regulations for the use of nano-particles. But the properties of artificial silver, silicates, titanium oxide and zinc oxide, as well as a number of organic nanoparticles are largely unknown in the context of size, structure and above all, in interrelationship with organic molecules. The opto-electrochemical sensor developed by the IN-STANT project aims to change that. The European Union is providing €3.8m in funding for the pro-ject, with €1m to be invested in the Tübingen research. The project is also linked with European Initiative NanoSafety Cluster, which will further integrate the EU-funded projects SMART-NANO and NANODETECTOR later this year.
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.