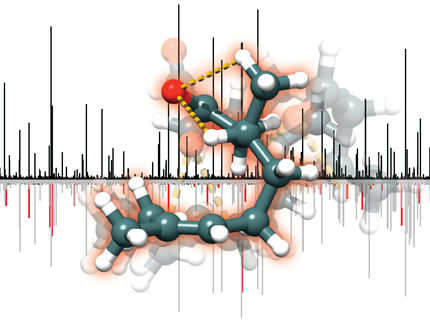
Odorant shape and vibration likely lead to olfaction satisfaction
A new study of the sense of smell lends support to a controversial theory of olfaction: Our noses can distinguish both the shape and the vibrational characteristics of odorant molecules.
The study, in the journal Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, demonstrates the feasibility of the theory – first proposed decades ago – that the vibration of an odorant molecule's chemical bonds – the wagging, stretching and rocking of the links between atoms – contributes to our ability to distinguish one smelly thing from another.
"The theory goes that when the right odorant binds to its receptor, the odorant's molecular vibration allows electrons to transfer from one part of the receptor to another," said University of Illinois physics and Beckman Institute professor Klaus Schulten, who conducted the analysis with postdoctoral researcher Ilia Solov'yov and graduate student Po-Yao Chang. "This electron transfer appears to fine-tune the signal the receptor receives."
Many who study olfaction maintain that odorant receptors recognize only an odorant's shape and surface characteristics. They dismiss the idea that molecular vibration has anything to do with it, Schulten said. Likewise, some proponents of the vibrational theory think that molecular vibration only, and not shape, guides the sense of smell. Schulten and his colleagues belong to a "third camp" that sees evidence for both, he said.
The vibrational theory of olfaction is supported by studies showing that insects, humans and other animals can tell the difference between two versions of the same odorant molecule – a normal one and an identical one with deuterium atoms substituted for each of the hydrogens. The deuterated and normal versions of the odorant have the same shape and surface characteristics, and yet humans and other animals can smell the difference, Schulten said.
"The question then is of course, for scientists, how does this happen?" he said.
To answer this question, Schulten turned to the work of a former colleague at Illinois, Rudolph Marcus, a chemist (now at Caltech) who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1992 for his insights into electron transfer, one of the most basic forms of a chemical reaction.
"Marcus realized that when electrons are being exchanged between molecules the process is coupled to the vibrations of the molecules involved," Schulten said. Marcus focused primarily on the low-frequency "rumblings" that occur as a result of molecular vibration in large molecules, Schulten said.
Odorant molecules are generally quite small, however, with a lot of high-frequency, high-energy vibrations, Schulten said. Some scientists have theorized that these high-frequency vibrations can, when an odorant binds to the right receptor, enhance the likelihood that an electron will transfer from one part of the receptor to another, sending an electrical signal that contributes to the detection of that odor.
Prior to the new study, no one had analyzed the energetics of the system to see if the vibrations of the odorant molecules – in the context of all the background vibrations that are part of the system – could actually promote electron transfer within the receptor. Schulten and his colleagues are the first to conduct such an analysis, he said.
"You can actually carry out quantum chemical calculations that determine very precisely the vibration of the molecule as well as the ability to couple it to electron transfer," Schulten said. The calculations indicate that such an interaction is energetically feasible, he said.
Odorant receptors are embedded in membranes and so are more difficult to study than other proteins. But previous research indicates that some receptors are metalloproteins, and "the metals in the proteins are pre-designed to transfer electrons," Schulten said. "We also see that there are other amino acid side groups that can accept an electron, so the electron can be transferred through the protein."
Like others before them, Schulten and his colleagues suggest that the odorant receptor contains both an electron donor and an electron acceptor, but that electron transfer occurs only when a specific odorant is bound to the receptor. The new calculations offer the first quantitative evidence that the odorant can in fact promote electron transfer.
Those who suggested that molecular vibration played a role in odorant recognition in previous studies "didn't know about Marcus' theory and they didn't do quantum chemical calculations," Schulten said. "They argued very much on principle (that it was possible). So we are saying now, yes, it is really possible even when you do the most complete and reliable calculations."
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Unexpected protein structure findings could lead to new therapies
Routine blood test predicts how long cancer patients will survive

Global guidelines to improve the quality of microscopy images in scientific publications

Breakthrough in protein research: Toolkit makes protein design faster and more accessible - What used to take weeks can now be completed in a day or less

Femtosecond-fieldoscopy accesses molecules fingerprints at near-infrared spectral range - "This research...has potential applications across various fields, including chemistry and biology, where precise molecular detection is essential"

Human environmental genome recovered in the absence of skeletal remains - Innovative approach permits the identification of DNA in samples of environmental material

Machine learning model uses blood tests to predict COVID-19 survival - Levels of 14 proteins in the blood of critically ill COVID-19 patients are associated with survival