New flexible, transparent, wearable biopatch, improves cellular observation, drug delivery
Minimally invasive patch delivers exact doses directly into cells, lessens pain, toxicity
Purdue University researchers have developed a new flexible and translucent base for silicon nanoneedle patches to deliver exact doses of biomolecules directly into cells and expand observational opportunities.
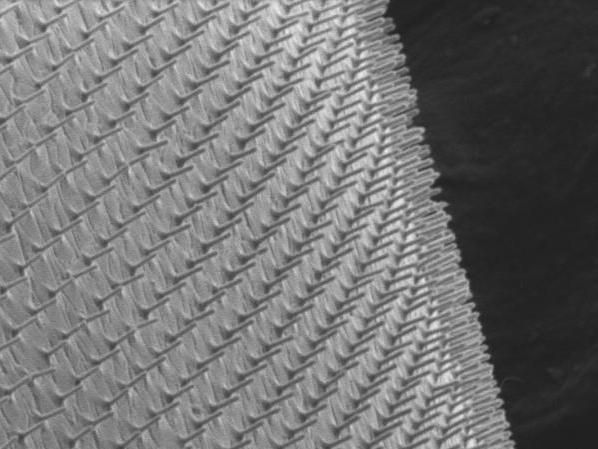
Purdue University researchers have created a drug delivery method using silicon nanoneedles with diameters 100 times smaller than a mosquito's needle. These nanoneedles are embedded in a stretchable and translucent elastomer patch that can be worn on the skin to deliver exact doses directly into cells.
Purdue image
"This means that eight or nine silicon nanoneedles can be injected into a single cell without significantly damaging a cell. So we can use these nanoneedles to deliver biomolecules into cells or even tissues with minimal invasiveness," said Chi Hwan Lee, an assistant professor in Purdue University's Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering and School of Mechanical Engineering.
A surgeon performs surgery on the back of a hand of a patient who has melanoma. Purdue researchers are developing a new flexible and translucent base for silicon patches to deliver exact doses of biomolecules directly into cells and expand observational opportunities. The researchers say skin cancer could be one of the applications for the patches.
Silicon nanoneedles patches are currently placed between skin, muscles or tissues where they deliver exact doses of biomolecules. Commercially available silicon nanoneedles patches are usually constructed on a rigid and opaque silicon wafer. The rigidity can cause discomfort and cannot be left in the body very long.
"These qualities are exactly opposite to the flexible, curved and soft surfaces of biological cells or tissues," Lee said.
Lee said the researchers have resolved that problem.
"To tackle this problem, we developed a method that enables physical transfer of vertically ordered silicon nanoneedles from their original silicon wafer to a bio-patch," Lee said. "This nanoneedle patch is not only flexible but also transparent, and therefore can also allow simultaneous real-time observation of the interaction between cells and nanoneedles." The collaborators from South Korea's Hanyang University and Purdue's Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering and School of Mechanical Engineering received joint support from the United States Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT to complete this study. The nanoneedles are partly embedded in a thin flexible and transparent bio-patch that can be worn on the skin and can deliver controlled doses of biomolecules.
Lee said the researchers hope to develop the patch's functionality to act as an external skin patch, lowering the pain, invasiveness and toxicity associated with long-term drug delivery.
In this technology's next iterations, Lee said the researchers plan to test operational validity of the patch's capabilities monitoring cellular electrical activity or treating cancerous tissue.
Original publication
Original publication
Kim, Hyungjun and Jang, Hanmin and Kim, Bongjoong and Kim, Min Ku and Wie, Dae Seung and Lee, Heung Soo and Kim, Dong Rip and Lee, Chi Hwan; "Flexible elastomer patch with vertical silicon nanoneedles for intracellular and intratissue nanoinjection of biomolecules"; Science Advances; 2018
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

CHSN-O, CN and N Elemental Analyzers by Velp Scientifica
State-of-the-art Elemental Analyzers for N, CN and CHSN-O in organic samples
Consistency, ease of use, and premium features for elemental analysis following official standards

HYPERION II by Bruker
FT-IR and IR laser imaging (QCL) microscope for research and development
Analyze macroscopic samples with microscopic resolution (5 µm) in seconds

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.




















































