Simulating cellular sorting processes
A plant or an animal cell uses numerous processes to sort and assemble tiny building blocks into larger molecules, to rebuild molecules or to dissolve them. Such processes depend on interactions between various cellular components and are pre-programmed at least in some of the building blocks. Using synthetic gel particles, scientists try to simulate these cellular procedures; however, mimicking the complexity of natural processes presents a formidable task for scientists. Researchers from the DWI – Leibniz Institute for Interactive Materials in Aachen and the University of Freiburg now developed a set of four different, micrometer-sized building blocks, which can self-sort and co-assemble into defined compositions and disassemble at the push of a button.
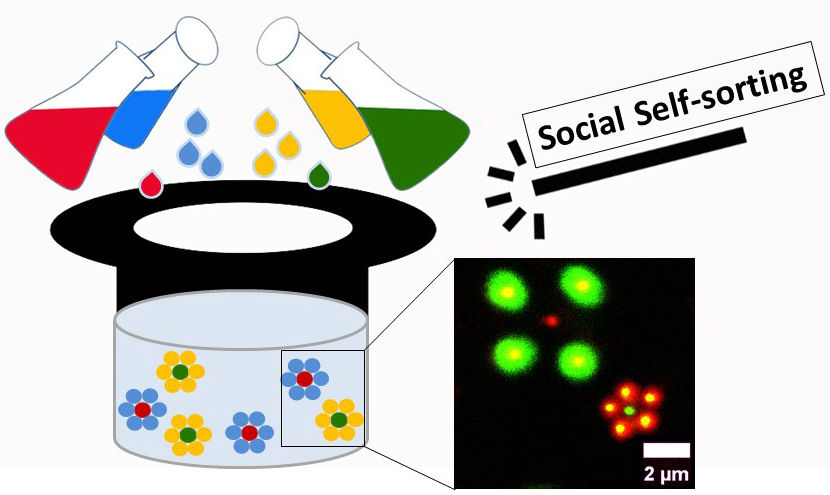
Scientists from the DWI – Leibniz Institute for Interactive Materials and the University of Freiburg synthesized four types of microgels, which self-assemble into different architectures. One example is a ‘social assembly’ of two types of microgels. The four types of microgels are schematically shown as colored droplets and as fluorescent particles in the microscopic image.
Andreas Walther, Universität Freiburg
A set of blue, red, green and yellow Lego bricks helps to visualize this research approach. It is very simple to build a multicolored object from these bricks, without considering the colors of the single bricks. To make it slightly more complicated, one could initially sort the bricks by their color and then build objects that are either blue, red, green or yellow. Such processes are referred to as ‘unsocial assemblies’ if they are driven by themselves. To make things even more complex, you could also build some objects from red and blue bricks and others from green and yellow bricks. These processes, if running simultaneously, are termed ‘social assemblies’.
The scientists from Aachen and Freiburg solved a similar task; however on a microscopic scale by using small gel particles instead of Lego bricks. These so-called microgels are water-rich, sponge-like gel particles, which can be chemically modified. “We used four different types of microgels for our experiments. The microgels can self-assemble in an ‘unsocial’ manner, staying amongst themselves, or co-assemble in a ‘social’ manner, with a second type of microgel,” explains Dr. Alexander Kühne from DWI. He coordinated this project together with Prof. Dr. Andreas Walther, a former DWI scientist who recently moved to the University of Freiburg.
The challenge of this project was to enable the microgels to distinguish between right and wrong partners. To achieve this, the scientists integrated molecular interactions so that only specific types of microgels would interact with each other – just like a key, which can only open a very specific lock. However, instead of keys and locks, the researchers applied switchable molecules that integrate into cyclic sugar moieties. Triggered by certain chemical conditions or by light the researchers could control the molecular shape and their interactions during the experiment. This way, the microgels can self-sort, self-assemble and disassemble at the push of a button.
“We use these types of experiments to get a better understanding of processes running in natural cells,” says Alexander Kühne. “In addition, progress in this field of research will eventually help us to develop biologically inspired, interactive materials.”
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.