Creating crystals from gold
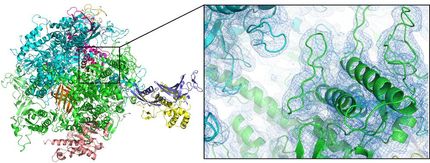
Crystals of an antibody peptide complex related to AIDS research
Scientists from Imperial College London have revealed how materials such as gold can help create protein Crystals. The team, from the Department of Surgery and Cancer , hope their findings could aid the discovery of new medicines and treatments. proteins are crucial to numerous functions in the body – yet scientists are still in the dark about what most of them look like.

A microscopic image of the crystals.
Imperial College of London
This is because the most powerful way of revealing the structure of proteins is to turn them into crystals, and then analyse these with X-rays. However, persuading proteins to turn into useful crystals is notoriously difficult. All crystals start from a conception stage when the first molecules come together; this is called nucleation. But reaching nucleation is often difficult as it requires a lot of energy – and many proteins simply can't overcome this barrier. Scientists also struggle to create medicines that bind to particular proteins –for instance a protein involved in cancer formation, if they don't know the protein's structure.
"How can you target a protein if you have no idea what it looks like? It’s like recognising a face in a crowd - you need a picture," explained Professor Naomi Chayen, lead author of the research.
Forcing molecules together with gold
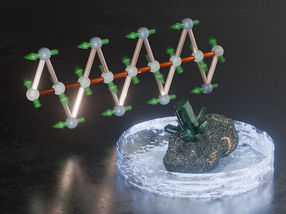
One technique for allowing proteins to reach their nucleation point is to trap them in tiny holes. This forces the molecules together, which helps them overcome the energy barrier needed to trigger the first crystal.
One material that scientists have found to be effective at growing crystals is gold. Creating many holes in the metal creates a substance called porous gold, which acts as a perfect environment for growing crystals, explained Professor Chayen:
“Gold doesn’t react with proteins, due to its inert nature, which makes it an ideal material to create crystals. Creating holes in the metal enable it to act a bit like coral, with each hole providing an ideal environment to harbour crystals.”
Creating crystals
In the latest research, the team investigated the best size hole needed to create crystals. They found that a variety of different sized holes produced the highest quality crystals. Most holes were around 5-10nm, just slightly larger than the width of a human hair.
Professor Chayen explained: “Imagine walking down a street with many potholes – some of the holes will be big enough for me to step out of, while some will be too small for my foot to fall into.
"However, some will be the exact size of my foot, and will trap me in them. This is the same principle as having different pore sizes – it allows us to trap different size protein molecules, enabling them to form crystals.”
She added that the findings which give a simple explanation of why, and under what conditions porous materials can induce protein crystal nucleation may help scientists design porous materials that would produce the highest quality crystals.
Original publication
Most read news

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.