Next-gen steel under the microscope
Next-generation steel and metal alloys are a step closer to reality, thanks to an international research project involving a University of Queensland scientist.
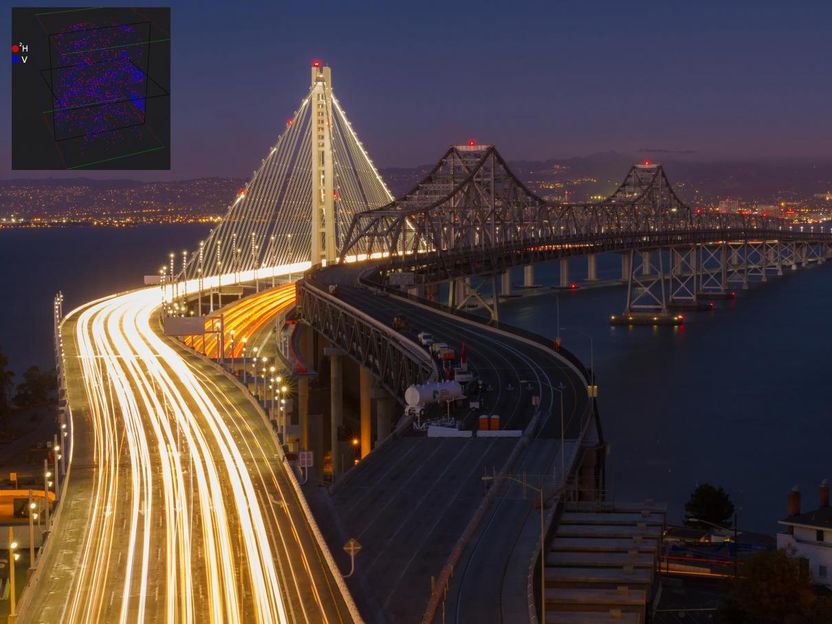

Eastern span of the San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge. The old and the new bridge, as seen at night from Yerba Buena Island to Oakland (mid-September 2013). The inset in the top left hand corner shows V Vanadium and 2H, Deuterium a hydrogen isotope (1 proton plus 1 neutron and 1 electron) as a Hydrogen substitute.
Photo credit Frank Schulenburg.
The work could overcome the problem of hydrogen alloy embrittlement that has led to catastrophic failures in major engineering and building projects.
UQ Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis Director Professor Roger Wepf said the problem had been recognised for almost 140 years.
"The current generation of these metals can suffer hydrogen embrittlement, where they become brittle and fracture due to the accidental introduction of hydrogen during manufacture and processing," he said.
"A major example of alloy embrittlement occurred in 2013, when bolts in the eastern span of the San Francisco-Oakland bridge failed tests during construction."
Professor Wepf said hydrogen was extremely volatile and diffused quickly.
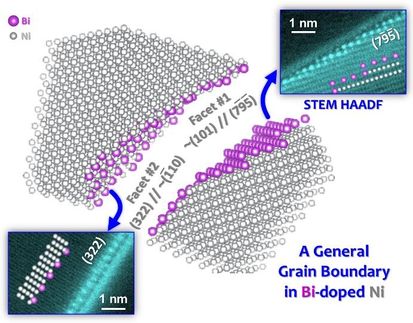
"Our research collaboration has, for the first time, localised and visualised hydrogen in steels and alloys," he said.
"This is essential for the development of new alloys with greater endurance."
"We have shown that it's possible to localise hydrogen at atomic resolution -- at the scale of a single atom -- or at a nanometre (less than one-billionth of a metre) scale by combining different technologies in a closed and protected workflow.
"These include state-of-the-art cryo electron microscopy freezing techniques, low-temperature sample preparation in a cryo focused ion beam microscope, and inert cryo-transfer.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.