Improved remote detection of hazardous radioactive substances
A recent study, affiliated with UNIST has introduced a method for the remote detection of hazardous radioactive substances. With the help of this newly-developed detection device, the detection of various types of radioactive materials can be done from a remote distance.
Professor Eunmi Choi's research team is posing for a group photo in their lab at UNIST. From left are WonJin Choi, Ashwini Sawant, Mun Seok Choe, Dongsung Kim, and Ingeun Lee.
UNIST
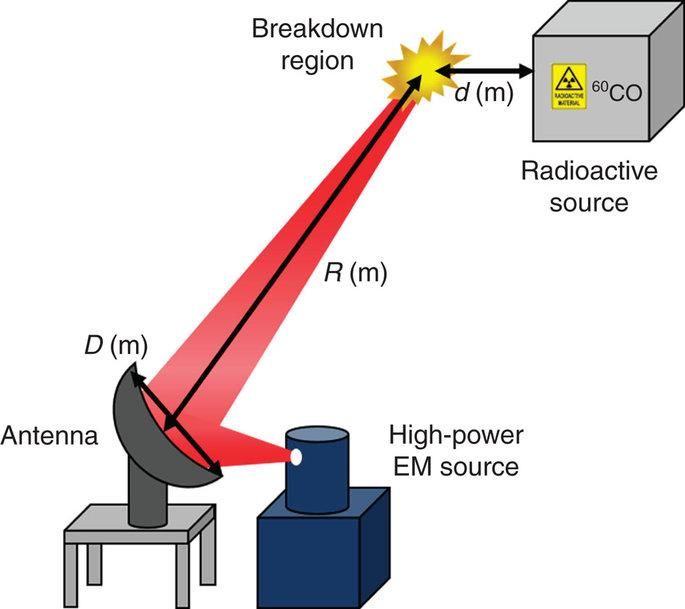
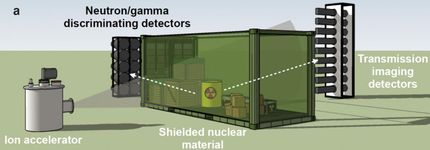
This is a schematic of a possible setup for the detection of radioactive material inside a container.
UNIST
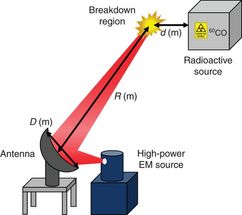
In their study Professor Eunmi Choi of Natural Science and her team demonstrated a method with higher sensitivity that uses high-power pulsed electromagnetic-waves to detect a radioactive source.
A substance is said to be radioactive if it contains atoms with unstable nuclei and gives out nuclear radiation in the form of alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. Uranium-235 (U-235) is an isotope of uranium widely used for nuclear power generation and, like all other radioactive isotopes used in medicine, it has been also employed for diagnosis and treatment of diseased organs and tumors. They are essential to mankind, but can have fatal consequences if it is accidentally leaked or used as a weapon.
Remote detection of radioactive materials is impossible when the measurement location is far from its source. Indeed, a typical radiation detectors, like Geiger-Muller counters have technical limitations in the remote detection of sources. For instance, they can detect 1 milli Curie (mCi) of Cobalt-60 (60Co) at a maximum distance of 3.5 metres, but are inefficient at measuring lower levels of radioactivity or at longer distances.
In the study, Professor Choi and her research team described the experimental demonstration of real-time radioactive material detection using a high-power pulsed millimetre-wave source. They demontrated the detection of 0.5 μg of cobalt-60 from 120 cm away, the maximum distance allowed by the laboratory setup.
"With the existing technologies, remote detection of radioactive materials is impossible when the measurement location is far from the radioactive source," says Dongsung Kim (Combined M.S./Ph.D. student of Physics), the first author of the study. "The detection sensitivity has been increased to 4,800 times, compared to the conventional theoretical sensitivity, enabling the detection of very small amounts of radiation."
"Depending on the equipment used, this method could scale to detect radioactivity at distances of at least tens of kilometers and possibly as far as 100 km," says Professor Choi.
Original publication

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.