Cheap and simple detection of neurotoxic chemicals
There is a limited amount of data on the global health impacts of pesticides, but many injuries and deaths worldwide can be attributed to their misuse. Pesticide contamination of food and water sources is a very serious problem, particularly in third world countries. The detection of these chemicals in the body using cheap and simple methods is a high priority.
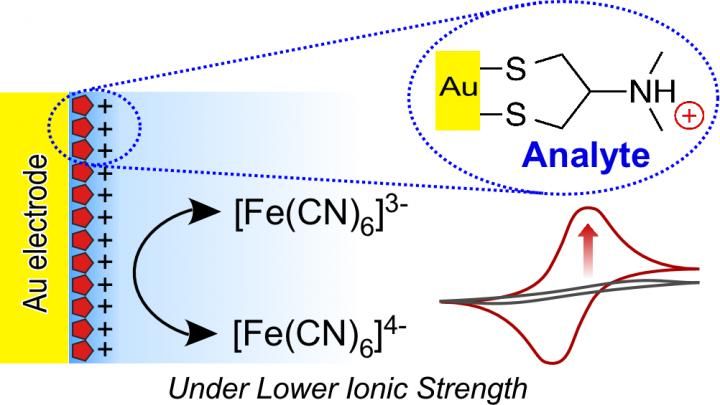
Nereistoxin adsorbed on the Au electrode surface promotes electron transfer between ferricyanide anions under unusually low ionic strength. (Image reprinted with permission from Shimada, H.; Noguchi, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Nishiyama, K.; Kitamura, Y. & Ihara, T., Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotoxic Agents Based on Their Electron Transfer Promotion Effect on an Au Electrode, Analytical Chemistry, American Chemical Society (ACS), 2017, 89, 5742-5747. DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04229. Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society.)
Professor Toshihiro Ihara
Relatively easy methods for analyzing fat soluble chemical compounds are already known. Water soluble pesticides, on the other hand, are slightly more complicated. They often need troublesome pretreatments such as extraction and derivatization prior to instrumental analysis such as gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS), which is why researchers from Kumamoto University , Konan University, and the Nagasaki Prefectural Police in Japan began examining simpler methods for toxin detection. They focused on Nereistoxin (NRT), a natural neurotoxin found in several pesticides. Typical analysis for NRT requires the use of high performance detectors.
The researchers showed that NRTs adsorbed on the surface of a gold electrode (via an Au-S bond) produced an easily distinguishable electrochemical response that, in the presence of a ferricyanide (0.5 millimolar (mM)) marker anion, was more sensitive than a non-treated gold electrode. A critical condition for this electrochemical technique is an abnormally low electrolyte concentration (1.0 mM KCl). Under these low concentrations, the bare electrode measured a current of nearly zero microamps, whereas an electrode with a surface NRT layer significantly accelerated the electrical response. The NRT layer compensated greatly for the handicap that comes with low KCl levels. This research is valuable not only for its usefulness as a simple and practical sensor, but also for providing a new principle in physical chemistry for sensors.
After confirming the feasibility of the method on other NRT-related neurotoxic pesticides (Cartap, Thiocyclam, and Bensultap) the researchers assessed its ability to detect neurotoxins in human serum. "We initially found an unidentified current when we tested the control serum, but it was quickly eliminated after washing the electrode with sodium hydroxide," said Professor Toshihiro Ihara, leader of the research project. "Fortunately, this was the only treatment required for the detection of 1-25 micro-grams of NRT per milliliter of human serum, which is the sensitivity required to detect NRT poisoning from pesticides and other sources. Other techniques are more complicated, take more time, or use much more complicated materials. We hope that our technique will open doors to other cheap and simple detection methods."
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Hiroshi Shimada, Shiori Noguchi, Masahiro Yamamoto, Katsuhiko Nishiyama, Yusuke Kitamura, and Toshihiro Ihara; "Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotoxic Agents Based on Their Electron Transfer Promotion Effect on an Au Electrode"; Analytical Chemistry; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.