Microarray rapid test speeds up detection in case of a Legionella pneumophila outbreak
In an outbreak of Legionnaires' disease, finding the exact source as quickly as possible is essential to preventing further infections. To date, a detailed analysis takes days. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich have now developed a rapid test that achieves the same result in about 35 minutes.
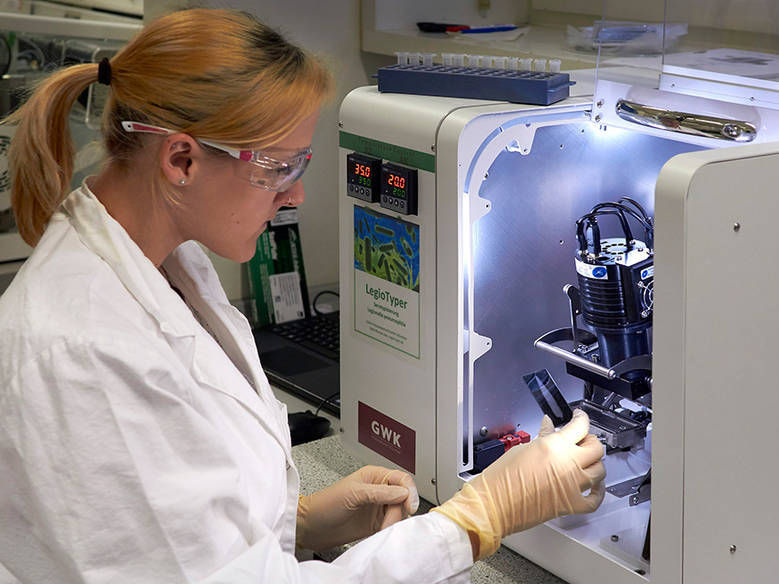

First author Catharina Kober with the LegioTyper-chip.
Jonas Bemetz / TUM
Legionella are rod-shaped bacteria that can cause life-threatening pneumonia in humans. They multiply in warm water and can be dispersed into the air via cooling towers, evaporative recooling systems and hot water systems.
The most dangerous among the almost 50 species of Legionella is Legionella pneumophila. It is responsible for 80 percent of all infections. When an outbreak occurs, the source of the germs must be identified as soon as possible to prevent further infections.
Similar to a paternity test, the origin of the outbreak is confirmed when the germs in the process water of a technical system exactly match those identified in the patient. However, often numerous systems must be tested in the process, and the requisite cultivation for the test takes around ten days.
Faster detection with antibodies
Meanwhile there is a rapid test for detecting the Legionella pathogen in the clinic. It identifies compounds of Legionella in the urine of patients. "Unfortunately, this quick test serves only as a first indication and is not suitable for screening the water of technical systems," says PD Dr. Michael Seidel, head of the research group at the Chair of Analytical Chemistry and Water Chemistry of the Technical University of Munich.
The team of scientists thus developed a measuring chip in the context of the "LegioTyper" project funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. This chip not only detects the dangerous pathogen Legionella pneumophila but also identifies which of the approximately 20 subtypes is present.
Fast, inexpensive and versatile
The foil-based measuring chip uses the microarray analysis platform MCR of the Munich company GWK GmbH. Using 20 different antibodies, the system provides a complete analysis within 34 minutes.
"Compared to previous measurements, the new method not only provides a huge speed advantage," says Michael Seidel, "but is also so cheap that we can use the chip in one-time applications."
The system can be deployed for environmental hygiene as well as clinical diagnostics. In combination with a second, DNA-based method, the system can even distinguish between dead and living Legionella pathogens. This allows the success of disinfection measures to be monitored. The project participants will present their system to the public for the first time at the Analytica 2018 trade fair in Munich.
Original publication
Wunderlich, A.; Torggler, C.; Elsaesser, D.; Lück, C.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M.; "Rapid quantification method for Legionella pneumophila in surface water"; Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry; 2016, 408(9), 2203-2213.
Kober, C.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M.; "Quantification of viable and non-viable Legionella spp. by heterogeneous asymmetric recombinase polymerase amplification (haRPA) on a flow-based chemiluminescence microarray"; Biosensors and Bioelectronics; 2018, 100, 49-55
Most read news
Original publication
Wunderlich, A.; Torggler, C.; Elsaesser, D.; Lück, C.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M.; "Rapid quantification method for Legionella pneumophila in surface water"; Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry; 2016, 408(9), 2203-2213.
Kober, C.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M.; "Quantification of viable and non-viable Legionella spp. by heterogeneous asymmetric recombinase polymerase amplification (haRPA) on a flow-based chemiluminescence microarray"; Biosensors and Bioelectronics; 2018, 100, 49-55
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.