A first look at interstitial fluid flow in the brain
Interstitial fluid transports nutrients and removes waste between the organs and tissues in our body. In the brain, interstitial fluid is thought to be composed of circulating cerebrospinal fluid, cellular waste and blood plasma, and past research has shown a link between interstitial fluid flow and an increased invasion rate of glioblastoma, or brain tumor, cells. A team of biomedical researchers and electrical engineers from the University of Virginia and Virginia Tech recently developed a new method to measure and reconstruct interstitial fluid flow velocities in the brain.
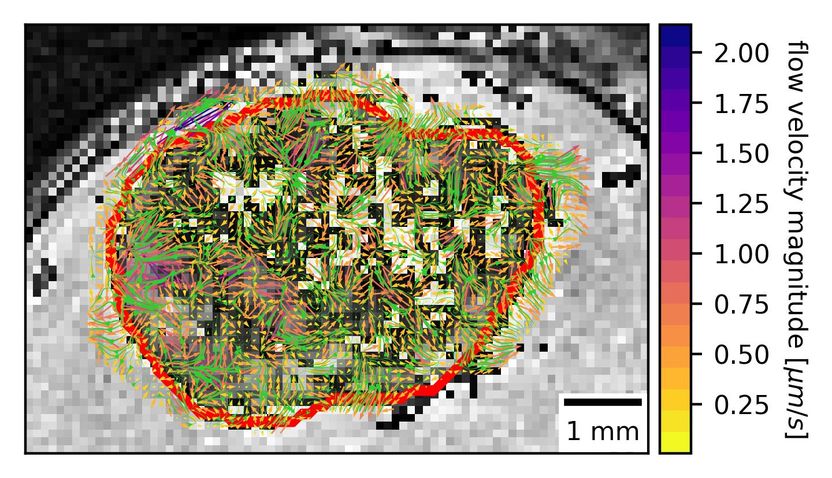
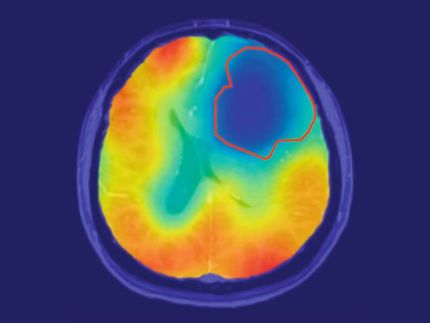
This MRI with contrast shows heterogenous interstitial fluid flow in glioblastoma. The tumor border is outlined in red.
Kingsmore et al.
This method gives researchers a first look at interstitial fluid flow dynamics in glioma models, and the technique can readily translate to clinical models already using contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The team built on an existing dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI technique that's already frequently used in clinics to track tumor growth and movement. "We are excited about our technique because we could potentially translate it to patient data that already exists and look at interstitial fluid motion in those patients," said Jennifer Munson, a lead author on the paper.
Munson touted the team's rigorous validation approach in silico and in vitro. First, the team developed an in vitro model of interstitial fluid flow moving through extracellular space by placing fluid on top of a hydrogel and using MRI to measure how the fluid flowed from top to bottom. Then, they validated their computational model against their experimental measurements.
To further validate their technique, Daniel Abler and Russell Rockne, who are co-authors on the paper, created phantom fluid "flow field," in a computer and then reconstructed that flow using their new imaging methodology. Finally, the team implanted patient-derived glioma cells in mice and examined the mouse tumors using MRI to visualize a real flow field.
The team was surprised to find high variability in the flow's rate and magnitude. "There's been this classical idea that a tumor develops and there's this equivalent flow rate going out in all directions like a sphere," Munson said. "Our method and our visualization approach and modeling show that that's a large oversimplification and we have a very heterogenous system. Sometimes flow is going out, or in, or along the side."
One day, this technique could potentially help researchers predict how a tumor might grow and, therefore, improve cancer treatments. More immediately, the team plans to use their established method "to understand the relationship between the fluid velocities and the growth of the tumors," Munson said.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Kathryn M. Kingsmore, Andrea Vaccari, Daniel Abler, Sophia X. Cui, Frederick H. Epstein, Russell C. Rockne, Scott T. Acton, and Jennifer M. Munson; "MRI analysis to map interstitial flow in the brain tumor microenvironment"; APL Bioengineering; 2018
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.