New chemical tools to modify and study biomolecules
Understanding the structure and metabolism of cells and living organisms is essential for the development of new drugs and diagnostics. The availability of chemical tools that allow scientists to edit biomolecules, like proteins, with atom-level resolution have greatly contributed to the progress of chemical biology.
An illustration of the chemical reaction developed in the study.
J. Waser/B. Fierz (EPFL)
Proteins are macromolecules constructed from a set of twenty chemically different amino acids. One key approach to modify proteins is to react with the sulfur atom in the amino acid cysteine. However, current methods are still problematic in terms of efficiency, selectivity, and stability of the final product (the "adduct").
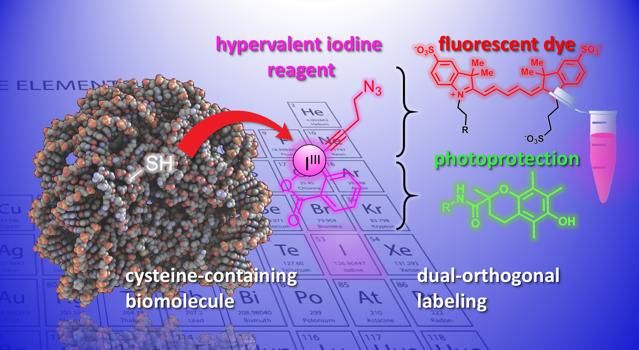
Now, the labs of Jérôme Waser and Beat Fierz at EPFL's Institute of Chemical Sciences and Engineering have developed a new method for modifying cysteines on peptides and proteins. The method uses a group of highly reactive organic molecules, the ethynylbenziodoxolones (EBXs). What makes EBXs highly reactive is that they contain an iodine atom bound to three substituent groups. This non-natural situation leads to high reactivity in these so-called "hypervalent iodine" reagents.
For the first time, the researchers were able to generate a simple biomolecule-EBX adduct while keeping their reactive iodine group in the final molecule. The reaction can be easily performed by a non-expert under standard physiological conditions.
The end product are protein-hypervalent iodine reagent chimeras that can act as dual attachment points for two new chemical groups, opening up new opportunities for the study of biological processes.
"One new functionality can be introduced via 'click-chemistry', a well-established reaction in chemical biology," says Waser. "Using a palladium catalys, another selective modification can be achieved at the reactive iodine atom- what we would call a 'biorthogonal' functionality, as it does not exist in nature." Introducing such exotic reactive groups into biomolecules is currently one of the most important tools in chemical biology, as it allows the study of biological processes without interfering with them.
The scientists demonstrated the potential of the method by introducing a diverse set of chemical groups into biomolecules. For example, the scientists used the dual handle to attach a fluorescent dye and a photoprotecting group into a neuropeptide simultaneously. Combining them improves the dye's photostability, and enables high-resolution, single-molecule imaging of molecular interactions.
Beyond peptides, they further modified small proteins, and even large protein-DNA complexes, so-called nucleosomes. As nucleosomes organize the genome, labeling them with fluorescent dyes can help track them to decipher how nature regulates gene expression.
"What we developed here is a new method for modifying proteins based on fundamental studies of chemical reactivity," says Fierz. "We have already used it to modify of histones, and carried out fluorescence experiments on living cells. With these examples, we have set the foundation for a better understanding of biological processes."
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.