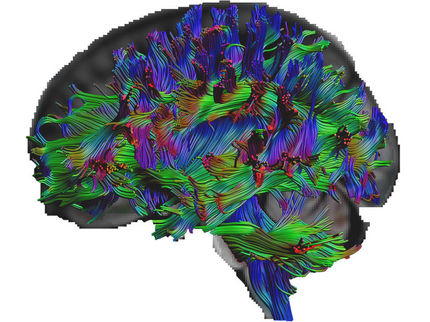
Brain mages of previously unattainable quality
A new three-dimensional model of the brain now provides in-depth insights into the human control centre. It allows us to see and understand the complicated structure of the brain on a microscopic level in all three spatial dimensions for the first time. This is made possible using images with a resolution of 20 micrometres – the size of a neuron, or less than half the diameter of a human hair. Jülich researchers headed by neuroscientist Prof. Dr. Katrin Amunts and their colleagues from Montreal (Canada) have worked on the freely accessible model for five years.
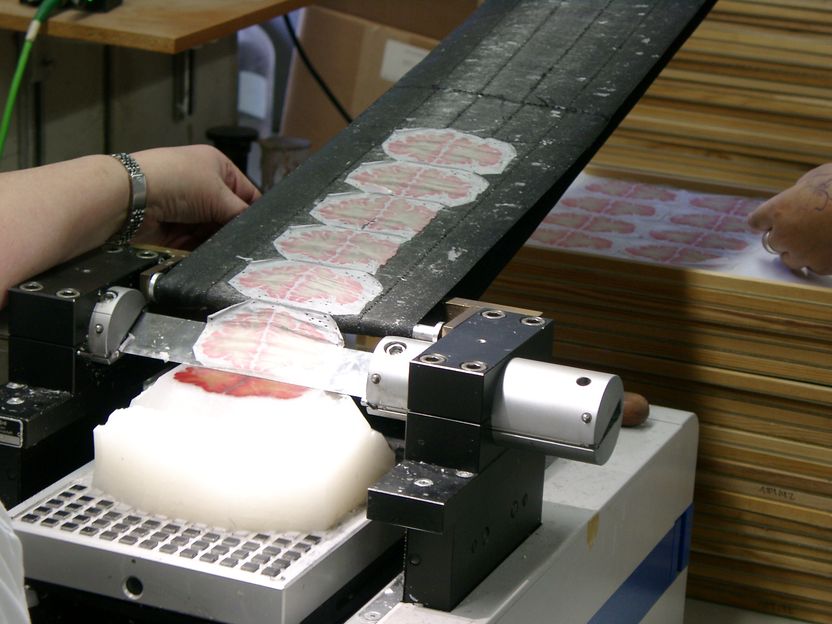

Researchers use a special tool called a microtome to cut sections from a brain preserved in paraffin wax into tiny slivers 20-micrometers thick in a handout photo.
Amunts, Zilles, Evans et al.
"BigBrain helps us to generate new knowledge on the healthy and also the diseased brain," says Katrin Amunts, director at the Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-1) and the C. and O. Vogt Institute of Brain Research at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf. For example: "As a consequence of its evolution, the human cerebral cortex is very heavily folded," says the neuroscientist. She explains that this is the reason why, in some areas, the thickness of the cerebral cortex can only be determined very imprecisely using imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging. However, the thickness of the cortex changes in the course of a lifetime and is also affected by neurodegenerative processes, such as those associated with Alzheimer’s disease. "With the help of our high-resolution brain model, we can now gain a new understanding of the normal structure of different functional areas of the brain, such as the motor cortex or a region that is important for learning and memory, and we can also measure numerous structural properties," explains Katrin Amunts. This will contribute to the precise identification and evaluation of changes in the brains of patients.
Information from thousands of tissue samples
The three-dimensional virtual brain is based on information from more than 7,400 tissue sections, each of them a mere 20 micrometres thick, that were obtained from a human brain. "We started off in Düsseldorf more than five years ago," says co-initiator Prof. Karl Zilles, now a senior professor in JARA-BRAIN, the brain research cooperation between Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University. Each individual tissue section was scanned at Forschungszentrum Jülich and then reconstructed in three dimensions with supercomputers. "It’s an extremely difficult and complex task to work with these ultrathin, fragile tissue samples," says Katrin Amunts. Cutting the extremely thin sections can cause tears or folds that have to be ‘repaired’ in the digitized versions by means of modern image processing tools, explains the researcher. In order to process the huge data sets produced, reconstruct them in three dimensions, and evaluate them, the scientists needed powerful supercomputers in Canada and at Jülich.
Human Brain Project benefits from BigBrain
The findings obtained from BigBrain will also be used in the European large-scale Human Brain Project (HBP), which includes Jülich experts specializing in neuroscience and information technology. Together with other researchers from more than 80 scientific institutions in 23 countries, they plan to simulate the entire human brain, from the molecular level to the interaction of entire brain regions, on a supercomputer of the future within the next ten years. In addition to their neuroscientific findings, the Jülich scientists will also contribute to HBP with their innovative software tools. With these tools, data from other brain models can be integrated into the freely accessible software tool BigBrain and be made available to the scientific community.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.