Prototype electrolyte sensor to provide immediate read-outs
Painless wearable microneedle device may reduce trips to doctors' offices
Patients trying to navigate today's complex medical system with its costly laboratory analyses might prefer a pain-free home diagnostic device, worn on the wrist, that can analyze, continuously record and immediately remedy low electrolyte levels.
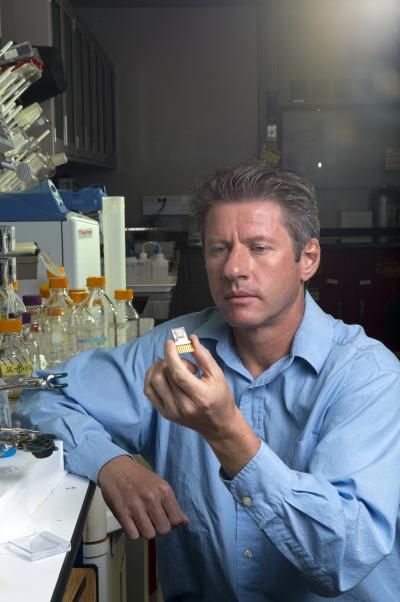

Sandia National Laboratories researcher Ronen Polsky holds a prototype of a microneedle fluidic chip device able to selectively detect and painlessly measure electrolytes in the interstitial fluids that bathe skin cells. It features nine sampling needles, each only 800 millionths of a meter (microns) in height, and beneath them, a fluidic channel that can draw interstitial fluid over nine gold disk electrodes. Each disk can be tailored to detect a different analyte. The visible rectangular gold pads are electrical contacts.
Randy Montoya
Runners, athletes in other strenuous sports and soldiers on long missions also might prefer immediate knowledge of their electrolytic states as an aid to improved performance. Electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, magnesium and other salts are key in carrying nerve impulses that tell the heart and other muscles when to contract or relax.
In response to this need, Sandia National Laboratories researcher Ronen Polsky and colleagues are patenting a prototype model that can analyze various electrolyte levels on the spot, yet fit in a palm or be worn on a wrist. The device, when commercially available, could decrease the time ordinary citizens, athletes and the military must spend in emergency rooms, lab testing facilities or doctors' offices.
"This is the future of personalized health care," said Polsky. "These wearable technologies are just starting to come out in different forms. It's inevitable that people will go there."
The device is painless because it employs microneedles so tiny they don't traumatize nerves when pressed into the skin. It also samples only interstitial fluid — the liquid between skin cells. Thus the device has the potential for long-term, noninvasive use.
In a paper published in of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Polsky, Sandia colleagues and University of North Carolina and North Carolina State University graduate student Phil Miller describe using a laser to create strong hollow microneedles that suck nearly infinitesimal amounts of colorless fluid from just beneath the skin's surface. The paper demonstrates that tiny amounts of potassium passed unhindered through the microneedle pores into a fluidic cartridge containing carbon electrodes. These measured the amount of this key electrolyte without being confused by the presence of other electrolytes in the fluid.
Miller said it's easy to change the selectivity of the carbon electrodes to detect and measure other such electrolytes like sodium or calcium in the same device. "We want to make the device wearable, noninvasive, and with real-time readout to constantly measure things a doctor might normally order for laboratory tests," he said.
Eventually the researchers envision a "sense-respond" device where some needles can read electrolytes while other needles, on demand, send electrolytes to make up for deficiencies.
Most read news
Organizations

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.