Microhotplates for a smart gas sensor
gas sensors used for leakage alerts and air quality monitoring are essential in our daily lives. Towards a ubiquitous society, smart gas sensors, which perform signal processing and communication besides sensing, have attracted much attention. In addition, integrating these functions into a single chip leads to low-cost and miniature smart gas-sensing systems.
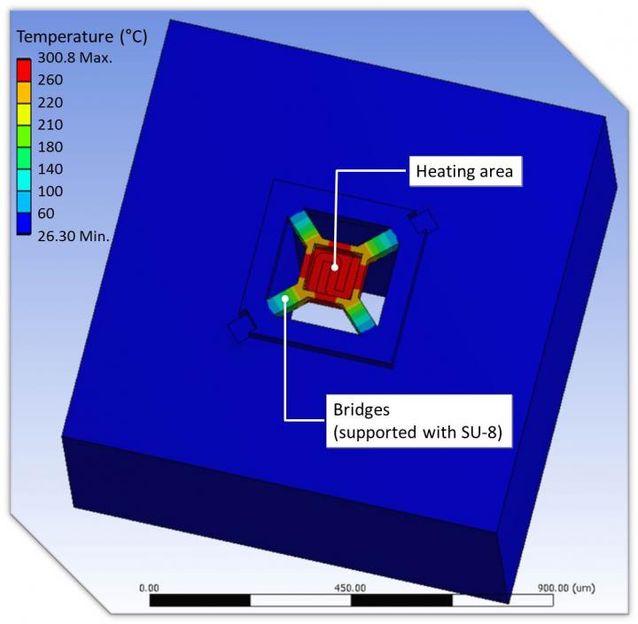
This is a simulation result of the temperature distribution in the proposed micro-hotplate.
COPYRIGHT (C) TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Semiconductor gas sensors, which are the most widely used gas sensors, require a sensor material to be heated to several hundreds of degree Celsius. Therefore, in order to integrate these gas sensors with electronic circuits, a micro-hotplate (MHP), which is a MEMS-based heating structure, is required to thermally isolate the sensor and the circuits. The MHP is generally mechanically unstable, and there exists a tradeoff between the mechanical stability and thermal isolation property.
Recently, a research team at the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology proposed the employment of SU-8 as a supporting material for the MHP, in order to improve the mechanical stability, while ensuring the thermal isolation property. Furthermore, SU-8 is a polymer material that is widely used for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and has good mechanical stability and low thermal conductivity. The researchers fabricated the MHP and investigated its heating characteristics.
The first author Assistant Professor, Tatsuya Iwata, said that "By using a thick polymer film, it is possible to realize both the mechanical stability and high thermal isolation property. Furthermore, although we have to evaluate the mechanical stability, this device is promising for smart gas sensors."
"Mechanical stability is one of the major concerns for fabricating an MHP. Using a polymer material for such microhotplates seems to be an eccentric approach, but surprisingly, it went well. Moreover, this device will boost our study to develop multimodal sensors, which are multifunctional integrated sensors including gas sensors," said Professor Kazuaki Sawada.
The fabricated MHP consists of a heating membrane with an area of 140 μm × 140 μm, and a 33-μm-thick SU-8 layer deposited on its bridges. The simulation confirmed that the MHP displayed good thermal isolation properties (Fig. 1). The MHP temperature was found to reach 550 °C at 5V. Moreover, the power consumption of the MHP approximately corresponded to 13.9 mW for heating to 300 °C, which is comparable with the power consumption reported in the previous studies. Furthermore, a stable operation under a constant voltage was observed for 100 min.
Owing to the thick SU-8 layer, the MHP does not need the strict control of the stress that occurs inside the membrane during the fabrication process. This feature, together with the good thermal isolation property, enables the flexible layout design of the chip, and therefore, the MHP is beneficial to a miniature smart gas sensor chip. The researchers will advance their study to realize such smart gas sensors.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
T Iwata, W P C Soo, K Matsuda, K Takahashi, M Ishida and K Sawada; "Design, fabrication, and characterization of bridge-type micro-hotplates with an SU-8 supporting layer for a smart gas sensing system"; Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.



















![[Fe]-hydrogenase catalysis visualized using para-hydrogen-enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy](https://img.chemie.de/Portal/News/675fd46b9b54f_sBuG8s4sS.png?tr=w-712,h-534,cm-extract,x-0,y-16:n-xl)