Unexpected carbon composition discovered in world's oldest diamonds
Did life on earth begin earlier than we have hitherto believed?
While examining the oldest diamonds in the world, a group of researchers, including Martina Menneken and Dr. Thorsten Geisler from the University of Münster (Institute of Mineralogy), have found evidence that life may have existed 4.25 billion years ago. Up to now, scientists have assumed that the first living cells came into being around 3.5 billion years ago. The prestigious magazine "Nature" has published the results in its current edition dated July 3rd, 2008.
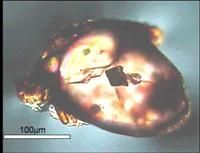
Diamont inclusion in zircon
Martina Menneken
Martina Menneken and her colleagues had already made news in 2007 when they discovered the oldest diamonds in the world. Since then a team consisting of scientists from Australia, Sweden and Münster have been continuing their analysis of the diamond and graphite inclusions in zircons from western Australia which are only a few micrometres in size and up to 4.25 billion years old. In the course of their work the researchers have found some unexpectedly low content of the heavy carbon isotope C-13. Small amounts of this isotope are typical of carbon originating from organic material.
With the aid of a secondary ion mass spectrometer the scientists have measured the proportions of various carbon isotopes (C-12 to C-13) in the inclusions in order to get more information about where the carbon came from and how the diamond and graphite inclusions arose. The proportions measured range from typical values found in the earth's crust to values characterized by an extremely low amount of the heavy C-13 isotope.
"The composition of the carbon isotopes is an indication that life may have existed 4.25 billion years ago," says Martina Menneken. However, abiogenic chemical reactions may also have caused low amounts of heavy carbon. What is certain is that very soon after the formation of the earth 4.56 billion years ago there must have existed on earth a carbon reservoir with extremely low amounts of C-13.
"Our data do not prove the existence of life 4.25 billion years ago," says Menneken, "but they do raise the question of how this unexpected carbon composition arose." The presence of living organisms is one possible explanation. If it should turn out to be true, the history of life would have to be rewritten.
Original publication: Nemchin et al.: A light carbon reservoir recorded in zircon-hosted diamond from the Jack Hills. Nature 454, 92-95, 2008
These products might interest you
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry enables us to detect and identify molecules and reveal their structure. Whether in chemistry, biochemistry or forensics - mass spectrometry opens up unexpected insights into the composition of our world. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of mass spectrometry!

Topic World Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry enables us to detect and identify molecules and reveal their structure. Whether in chemistry, biochemistry or forensics - mass spectrometry opens up unexpected insights into the composition of our world. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of mass spectrometry!