Raman’s narrower fingerprint set to broaden utility of flow cytometry
Andor Technology plc announced that researchers have successfully tested the first proof-of-concept of a Raman Spectral Flow Cytometer (SFC), thanks to its Electron Multiplying CCD (EMCCD) camera NewtonEM.
Raman Spectral Flow Cytometry promises to revolutionise cell characterisation by allowing hundreds of variables to be observed simultaneously. It will also make it far easier to distinguish between different cell types given the narrow spectral fingerprint compared to fluorescence. The group hopes this new technique will eventually complement traditional flow cytometry, which can only currently characterise cells using a maximum of 19 parameters, with traditional side scatter and different fluorescent colours techniques.
Researchers from the La Jolla Bioengineering Institute have successfully developed their new design of high-resolution flow cytometer by incorporating a highly-sensitive EMCCD camera from Andor. Previous spectral flow cytometer designs had used single point detectors such as photomultipliers, restricting instantaneous spectral information.
Raman spectra have narrower wavelength bands than fluorescent labels meaning hundreds of separate variables can be measured without overlap between wavelengths. Fluorescent labels attached to cells in traditional flow cytometry emit over a wide range of wavelengths, so there is a limit to the number that can be used.
The Raman signal in the group’s Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) technique is boosted by binding metal nanoparticles to the cells. The SERS emissions are measured using Andor’s camera. In time, it is hoped that Raman spectral information could also be used to complement and improve the ability of flow cytometers to sort cells as well as identify different cells.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department research and development

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.

Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!
Last viewed contents
Gyros and SCRUM sign distribution agreement for the Japanese market

Smart formulation in food technology - Harnessing infrared spectroscopy for consistent and predictable apple puree quality

Adulterated animal-based foods to become easier to detect in future
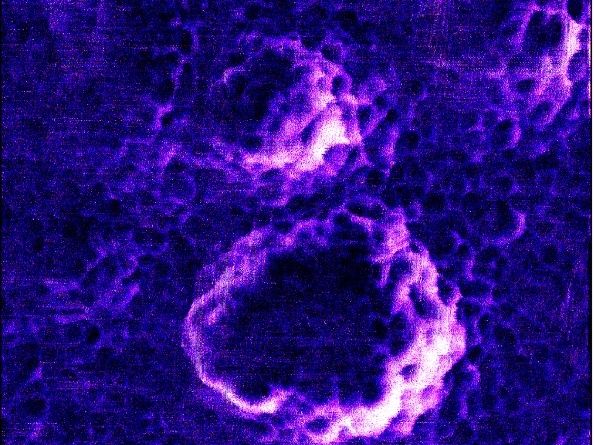
Observed live for the first time: photocatalysts switch off a virus - Whitening agent titanium dioxide kills viruses – now researchers see it at work at the nanoscale