Toilet paper sensors
Tissue paper sensors show promise for health care, entertainment, robotics
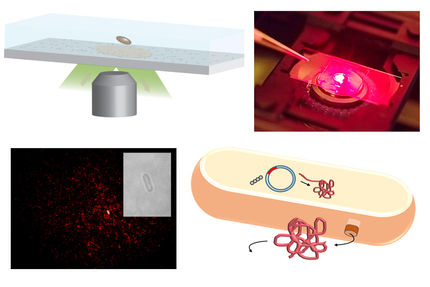
University of Washington engineers have turned tissue paper – similar to toilet tissue – into a new kind of wearable sensor that can detect a pulse, a blink of an eye and other human movement. The sensor is light, flexible and inexpensive, with potential applications in health care, entertainment and robotics.

University of Washington graduate student, Jinyuan Zhang, demonstrates how wearable sensors can track eye movement.
Dennis R. Wise/University of Washington
The technology shows that by tearing tissue paper that’s loaded with nanocomposites and breaking the paper’s fibers, the paper acts as a sensor. It can detect a heartbeat, finger force, finger movement, eyeball movement and more, said Jae-Hyun Chung, a UW associate professor of mechanical engineering and senior author of the research.
“The major innovation is a disposable wearable sensor made with cheap tissue paper,” said Chung. “When we break the specimen, it will work as a sensor.”
These small, Band Aid-sized sensors could have a variety of applications in various fields. For example, monitoring a person’s gait or the movement of their eyes can be used to inspect brain function or a game player’s actions. The sensor could track how a special-needs child walks in a home test, sparing the child the need for hospital visits. Or the sensors could be used in occupational therapy for seniors.
“They can use these sensors and after one-time use, they can be thrown away,” said Chung.
In their research, the scientists used paper similar to toilet tissue. The paper – nothing more than conventional paper towels – is then doused with carbon nanotube-laced water. Carbon nanotubes are tiny materials that create electrical conductivity. Each piece of tissue paper has both horizontal and vertical fibers, so when the paper is torn, the direction of the tear informs the sensor of what’s happened. To trace eye movement, they’re attached to a person’s reading glasses.
For now, the work has been contained to a laboratory, and researchers are hoping to find a suitable commercial use. A provisional patent was filed in December 2017.
The paper’s lead author is UW College of Engineering graduate student Jinyuan Zhang. Other co-authors include undergraduate student Cerwyn Chiew; mechanical engineering professors Minoru Taya and Dayong Gao; aeronautics and astronautics professor Jinkyu Yang and postdoctoral scholar Gil-Yong Lee, all of the UW; and graduate student Fabrice Fondjo and professor Jong-Hoon Kim of Washington State University Vancouver.
Original publication
Original publication
Jinyuan Zhang, Gil‐Yong Lee, Chiew Cerwyn, Jinkyu Yang, Fabrice Fondjo, Jong‐Hoon Kim, Minoru Taya, Dayong Gao, Jae‐Hyun Chung; "Fracture‐Induced Mechanoelectrical Sensitivities of Paper‐Based Nanocomposites"; Adv. Mater. Technol.; 2018
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.