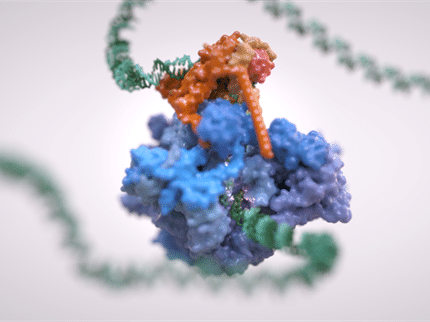
A 3D structure of 1918 influenza virus-like particles
virus-like particles (VLPs) are protein-based structures that mimic viruses and bind to antibodies. Because VLPs are not infectious, they show considerable promise as vaccine platforms for many viral diseases, including influenza. Realizing that fine details about influenza VLPs were scant, a team of researchers who specialize in visualizing molecular structures developed a 3D model based on the 1918 H1 pandemic influenza virus. They say their research could benefit VLP vaccine projects, targeting a range of viruses from HIV to Ebola and SARS coronavirus. The research was conducted by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and infectious diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
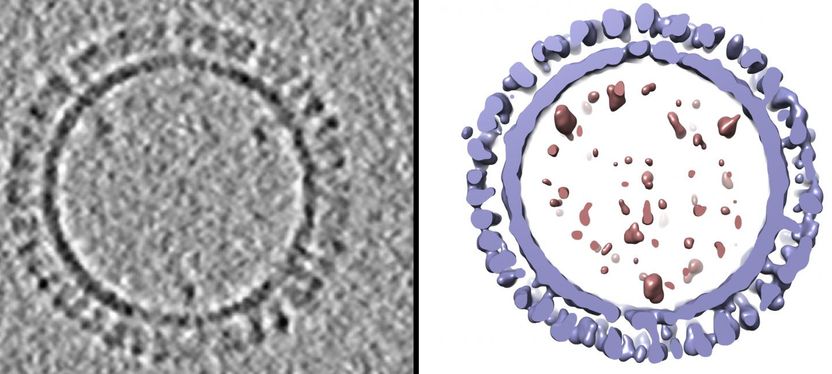
On the left is a 1918 H1 influenza virus-like particle (VLP) as seen by cryo-electron microscopy. On the right is the same VLP rendered in 3D with structural components computationally segmented and colored; hemagglutinin and membrane are light blue and internal components (molecular cargo) are red.
NIAID
Other researchers had produced VLPs for 1918 H1 influenza that successfully protected animals from different influenza viruses. The NIAID group prepared hundreds of such VLP samples and analyzed their structure with a technique called cryo-electron microscopy, which quick-freezes samples with glass-like clarity. They then sliced through those VLP 3D structures--like slicing through a loaf of bread--to analyze their internal structure, using computers to document the size and placement of key molecules. After averaging all their data, the group then created a 3D 1918 influenza VLP model.
The scientists found that about 90 percent of the VLPs are hemagglutinin (HA) proteins (by weight) found on the VLP surface. In contrast, HAs comprise less than half of the viral proteins of natural influenza viruses. The number and location of HA molecules may influence the efficacy of VLP vaccines, influencing the binding of antibodies to specific epitopes on the HA protein. Those antibodies can similarly bind live influenza viruses, preventing them from infecting cells.
The research group, in NIAID's Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, is continuing its work by comparing its VLP data to data from other natural influenza viruses. They believe the more that is understood about the molecular organization of influenza VLPs, the better scientists will be able to develop effective seasonal and universal influenza vaccines.
Original publication
These products might interest you
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous