Tokyo Institute of Technology research: Simplifying genetic codes to look back in time
Tokyo Institute of Technology researchers show simpler versions of the universal genetic code can still function in protein synthesis
Daisuke Kiga and co-workers at the Department of Computational Intelligence and Systems Science at Tokyo Institute of Technology, together with researchers across Japan, have shown that simpler versions of the universal genetic code, created by knocking out certain amino acids, can still function efficiently and accurately in protein synthesis. The researchers conducted experiments altering the genetic code in a test tube. They removed the amino acid tryptophan and discovered that the resulting simplified code could still generate proteins as before. By knocking out individual amino acids and observing the effects, scientists will be able to understand how early primordial organisms may have functioned and evolved. There will be also numerous applications for simplified genetic strains in laboratory experiments, which could potentially prevent non-natural genetically modified materials from entering the natural world.
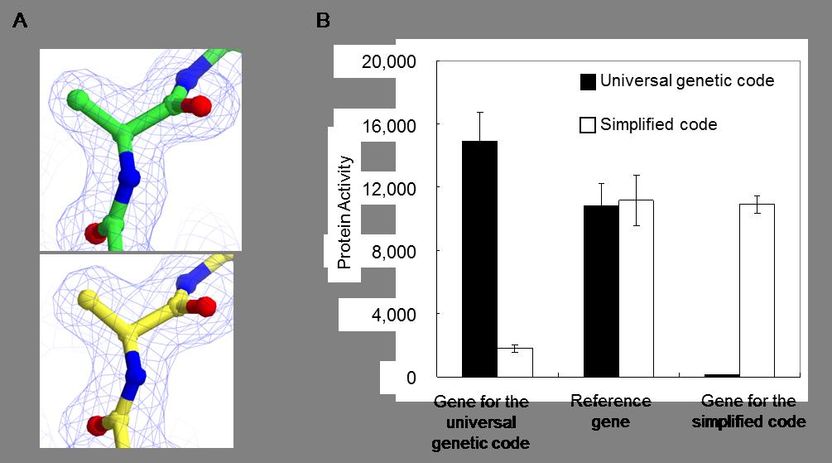
(A) Electron density maps. Upper panel: Alanine introduced by the GCU codon in the universal genetic code. Lower panel: Alanine introduced by the UGG codon in the simplified code. (B) Activity of proteins synthesized by the simplified and universal codes from the gene for each code.
Daisuke Kiga and co-workers of the Department of Computational Intelligence and Systems Science at Tokyo Institute of Technology, together with researchers across Japan, have shown that simpler versions of the universal genetic code - created by knocking out certain amino acids - can still function efficiently and accurately in protein synthesis. The researchers conducted cell-free experiments altering the genetic code.
All current life forms on Earth have 20 amino acids in their genetic code. However, scientists believe that this was not always the case, and that organisms evolved from simpler genetic codes with fewer amino acids. Amino acids are linked in accordance with codons – a 3-letter combination of the four base nucleotides (G, A, T and C) in a genetic code. There are 64 possible codons, and so most amino acids are produced by several different codons, except for tryptophan and methionine, which are generated by just one codon each. Tryptophan is thought to be the most recent amino acid to become part of the universal genetic code.
Kiga and his team took the codon for tryptophan, and reassigned it to code for the amino acid alanine instead. They discovered the resulting simplified code could still generate proteins as before. The researchers also reassigned another codon originally for the amino acid cysteine and replaced it with serine. This simplified code without cysteine was able to synthesise an active enzyme.
By knocking out individual amino acids and observing the effects, scientists will be able to understand how early primordial organisms may have functioned and evolved. There are also numerous applications for simplified genetic codes in laboratory experiments and clinical trials.
Before emergence of the current universal genetic code, primitive organisms that may have used only 19 amino acids could benefit from horizontal gene transfer, where cells transfer genetic material between one another. This is a key method used by bacteria to develop resistance to drugs. An organism with the current universal genetic code for 20 amino acids would have competitive advantages in its ability to synthesise proteins, but could not engage in genetic transfer with the rest of the population. Only when a suitably large gene pool of organisms with 20 amino acids is available could horizontal transfer occur between these life forms and they could then thrive. This implies that organisms with a simpler genetic code could be used as a barrier in laboratory experiments, preventing new genetically modified strains from escaping to the natural world.
Original publication
A. Kawahara-Kobayashi et al. Simplification of the genetic code: restricted diversity of genetically encoded amino acids. Nucleic Acids Research (2012).

























































