Sustainable production of pharmaceutical compounds
SmartCell project: Novel plant biotechnology
European scientists have made ground-breaking discoveries for improving the efficiency of the production of pharmaceuticals through plant biotechnology. Biotechnological production offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to the chemical synthesis of rare and complex pharmaceutical compounds currently isolated from plants. The results have been achieved in the European SmartCell project coordinated by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland.
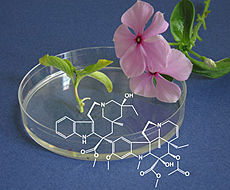
The main source of vinblastine and vincristine is the Madagascar periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus), also known as an ornamental plant. The SmartCell Consortium succeeded in elucidating the complete upstream segment of the biosynthetic pathway leading to these valuable anticancer pharmaceuticals, and thus creating the basis for their biotechnological production.
VTT
Several expensive anticancer alkaloid blockbusters used in chemotherapy, such as terpenoid indole alkaloids - vinblastine and vincristine, are currently extracted from the plant Catharanthus roseus (Madagascar periwinkle) at high price. These compounds are used to treat Hodgkin’s lymphoma, breast cancer, small-cell lung cancer and leukemia. Typically, very low levels accumulate in plant tissues, but chemical synthesis is not an economical alternative either due to their highly complex structures and specific stereochemical features. Internationally, much effort has been invested to develop more accessible and cost-effective sources of these drugs.
The biotechnological production of high-value plant-derived compounds using plant cell cultures is an attractive and sustainable alternative to extraction from whole plant material. However, the biosynthetic pathway leading to these compounds in plants is long and complex, with multiple enzymatic steps that are still largely uncharacterized at the genetic level. One of the main goals of the European Consortium SmartCell was to unravel the metabolic pathway leading to the periwinkle terpenoid indole alkaloids.
The SmartCell Consortium succeeded in elucidating the complete upstream segment of the terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis pathway, as described in a ground-breaking article published in the journal Nature Communications.
The complete pathway of twelve enzymes was reconstructed in tobacco plants, paving the way for cost-effective production of diverse therapeutic compounds. Moreover, cell culture technologies were developed, and the cultivation of the plant cells was scaled-up using bioreactors at VTT’s pilot laboratory in Finland.
“The use of plant cells as real green chemical factories is now becoming feasible for the first time. The technology developed and the experience gained on terpenoid indole alkaloids in this project can be utilized and applied to other compounds and plants as well”, says the project coordinator Dr Kirsi-Marja Oksman-Caldentey from VTT.
Original publication
K. Miettinen, L. Dong, N. Navrot, et al., The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus. Nature Communications. April 7th, 2014.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Extraction
Extraction is a fundamental process in the chemical laboratory that enables specific components to be isolated and concentrated from a mixture. Whether it's extracting active ingredients from natural products, removing impurities from synthesis products, or preparing analytical samples, extraction is a key step in achieving precise and efficient results in chemical research and analysis.

Topic world Extraction
Extraction is a fundamental process in the chemical laboratory that enables specific components to be isolated and concentrated from a mixture. Whether it's extracting active ingredients from natural products, removing impurities from synthesis products, or preparing analytical samples, extraction is a key step in achieving precise and efficient results in chemical research and analysis.