Tattoo-like sensor can detect glucose levels without a painful finger prick
Scientists have developed the first ultra-thin, flexible device that sticks to skin like a rub-on tattoo and can detect a person's glucose levels. The sensor, reported in a proof-of-concept study in the ACS journal Analytical Chemistry, has the potential to eliminate finger-pricking for many people with diabetes.
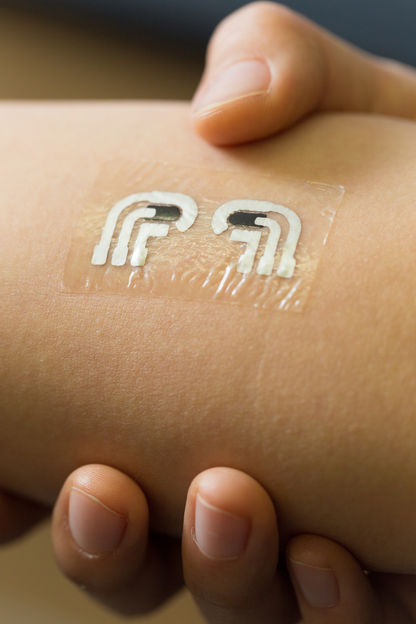
An ultra-thin sensor could help people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels without drawing blood.
Jacobs School of Engineering/UC San Diego
Joseph Wang and colleagues in San Diego note that diabetes affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. Many of these patients are instructed to monitor closely their blood glucose levels to manage the disease. But the standard way of checking glucose requires a prick to the finger to draw blood for testing. The pain associated with this technique can discourage people from keeping tabs on their glucose regularly. A glucose sensing wristband had been introduced to patients, but it caused skin irritation and was discontinued. Wang's team wanted to find a better approach.
The researchers made a wearable, non-irritating platform that can detect glucose in the fluid just under the skin based on integrating glucose extraction and electrochemical biosensing. Preliminary testing on seven healthy volunteers showed it was able to accurately determine glucose levels. The researchers conclude that the device could potentially be used for diabetes management and for other conditions such as kidney disease.
Original publication
"Tattoo-Based Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring: A Proof-of-Concept Study"; Analytical Chemistry
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.