NIST team proves bridge from conventional to molecular electronics possible
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have set the stage for building the "evolutionary link" between the microelectronics of today built from semiconductor compounds and future generations of devices made largely from complex organic molecules. In the Journal of the American Chemical Society, a NIST team demonstrates that a single layer of organic molecules can be assembled on the same sort of substrate used in conventional microchips.
The ability to use a silicon crystal substrate that is compatible with the industry-standard CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) manufacturing technology paves the way for hybrid CMOS-molecular device circuitry - the necessary precursor to a "beyond CMOS" totally molecular technology - to be fabricated in the near future.
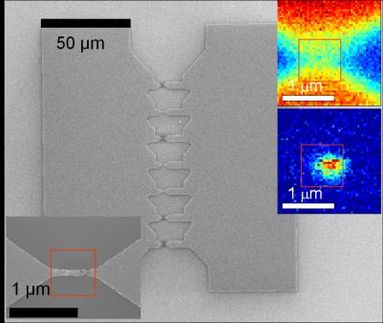
Scientists classify crystal structures by the particular plane or "face" cutting through the crystal that is exposed. Most research to date on silicon substrates for molecular electronic devices has been done with a crystal orientation that is convenient for organic molecules but incompatible with CMOS technologies. For their electronic device, the NIST team first demonstrated that a good quality monolayer of organic molecules could be assembled on the silicon orientation common to industrial CMOS fabrication, verifying this with extensive spectroscopic analysis.
They then went on to build a simple but working molecular electronic device - a resistor - using the same techniques. A single layer of simple chains of carbon atoms tethered on their ends with sulfur atoms were deposited in tiny 100-nanometer deep wells on the silicon substrate and capped with a layer of silver to form the top electrical contact. The use of silver is a departure from other molecular electronic studies where gold or aluminum has been used. Unlike the latter two elements, silver does not displace the monolayer or impede its ability to function.
The NIST team fabricated two molecular electronic devices, each with a different length of carbon chain populating the monolayer. Both devices successfully resisted electrical flow with the one possessing longer chains having the greater resistance as expected. A control device lacking the monolayer showed less resistance, proving that the other two units did function as nonlinear resistors.
The next step, the team reports, is to fabricate a CMOS-molecular hybrid circuit to show that molecular electronic components can work in harmony with current microelectronics technologies.
Original publication: N. Gergel-Hackett, C.D. Zangmeister, C.A. Hacker, L.J. Richter and C.A. Richter; "Demonstration of molecular assembly on Si (100) for CMOS-compatible molecular-based electronic devices."; Journal of the American Chemical Society 2008, Vol. 130, No. 13, pp 4259-4261.
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the analytics and lab tech industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.